Industry
Hemp has over 25,000 known uses including textiles, composites boards, cosmetics, paints, insulation, construction materials, sunscreen, paper, instrument bodies, plastics, food and medicine.
The hemp plant's stalks are made up of two layers: an outer layer of rope-like bast fibers and an inner layer of woody pith. For textile purposes, only the outer bast fiber layer of the Cannabis sativa stalk is used, while the inner woody layer is typically used for fuel, building materials, and animal bedding.
Hemp fibre is the strongest natural fibre known, weight for weight stronger than steel.
Construction
Hemp is becoming an increasingly popular material in the construction industry due to its sustainability, strength, and versatility.
Key uses for hemp in Construction include:
-
Hempcrete is a bio-composite material made from the inner woody core of the hemp plant mixed with a lime-based binder. It is used for construction and insulation purposes. Key benefits include:
Insulation: Excellent thermal and acoustic insulating properties as well as being air tight allowing it to meet todays building standards.
Sustainability: Hemp absorbs CO2 as it grows, and using it in construction helps sequester carbon.
Thermal mass.: hempcrete buildings change temperature slowly and therefore their heating and cooling energy demands are decreased compared to other insulation materials.
Both the insulation and thermal mass work together to make a more energy efficient build.
Regulation of Humidity: Hempcrete naturally regulates humidity, contributing to a healthier indoor environment.
Fire Resistance: Hempcrete is fire-resistant due to the lime binder.
Durability: It is resistant to pests and mold, enhancing the longevity of buildings.
-
Hemp fibers can be processed into high-density fiberboards, which are used similarly to traditional wood fiberboards. Benefits include:
Strength and Lightness: Hemp fiberboards are strong yet lighter than traditional wood boards.
Eco-friendly: Production of hemp fiberboard is less harmful to the environment compared to conventional wood products.
Low Emissions: Hemp fiberboards can be manufactured with fewer emissions and less energy consumption.
-
Hemp fibers are used to create insulation materials that offer several advantages:
Thermal Efficiency: High R-values for thermal insulation.
Breathability: Helps in maintaining healthy indoor air quality.
Non-Toxic: Hemp insulation is free from harmful chemicals found in some traditional insulation materials.
Recyclability: It is biodegradable and can be recycled.
-
Hemp can be combined with other materials to create composites and bioplastics used in various construction applications, such as:
Panels and Beams: Strong and lightweight components for building structures.
Fixtures and Fittings: Durable and sustainable alternatives to traditional plastic fittings.
-
Hemp fibers are incredibly strong and can be used to reinforce concrete and other materials, improving their tensile strength. This application is still in development but holds significant promise for the future of construction.
Benefits
Sustainability:
Eco-Friendly: Hemp is a renewable resource that grows quickly and requires fewer pesticides and herbicides than other crops.
Carbon Sequestration: Hemp absorbs more CO2 per hectare than most crops, making it beneficial for reducing carbon footprints.
Material Properties:
Strength: Hemp fibres are strong and durable.
Insulation: Hemp has excellent insulating properties, helping to regulate building temperatures and reduce energy costs.
Lightweight: Hemp-based materials are lighter than traditional construction materials, which can reduce transportation costs and energy
Limitations
Regulatory Issues:
Legal Restrictions: Varying laws around hemp cultivation can affect supply chains.
Building Codes: Not all building codes recognise hemp-based materials, which can limit their use in certain regions.
Cost:
Initial Investment: While hemp materials can reduce long-term costs, the initial investment can be higher than conventional materials.
Textiles
Hemp textiles refer to fabrics and products produced using the fibres from the hemp plant. Hemp has a long history of being used in textiles dating back 4,000 BC in China with some of its earliest known uses.
Hemp has many characteristics which make it ideal in textiles
Durability
fibers are known for their strength and long-lasting qualities
Sustainability
Hemp is a rapidly available resource with low water usage, few pesticides and improves soil health making it highly sustainable
Comfort
Hemp fabric is highly breathable, soft and moisture wicking.
Thermal Properties
Hemp fabric provides excellent thermal insulation keeping the wearer’s temperature well regulated in all seasons
Resistance
Hemp has high resistance to mould and mildew as well as efficiently providing resistance to UV rays
Biochar
Biochar is a form of charcoal produced by heating organic material (biomass) in the absence of oxygen, a process known as pyrolysis. It is primarily used as a soil amendment but has several other applications. Hemp biochar is a type of biochar produced specifically from the biomass of hemp plants.
Applications of Biochar
-
Hemp biochar can be used as a soil amendment to improve soil health, retain nutrients and balance PH making it more suitable for various types of crops..
Hemp biochar can facilitate healthier plant growth through enhancing soil structure, increasing water retention, and improving aeration
It can help retain nutrients in the soil, reducing the need for chemical fertilizers and preventing nutrient leaching.
-
By storing carbon in a stable form, hemp biochar can help in reducing the overall carbon footprint, contributing to climate change mitigation efforts.
-
Hemp biochar can absorb heavy metals and other contaminants from the soil, making it useful for soil remediation projects. It can be used in water filtration systems to remove impurities and contaminants from water sources.
-
Item description
-
Item description
-
Item description
Charcoal Biochar
Feedstock:
Wood-Based: Common Sources
Production Process:
Pyrolysis: Produced through the pyrolysis of wood biomass at high temperatures typically between 300°C and 700°C.
Traditional Methods: Often made using traditional charcoal-making methods, which may vary in efficiency and environmental impact.
Properties:
High Carbon Content.
Porosity: Varies depending on the type of wood and pyrolysis conditions but generally has a high surface area.
Nutrient Content: Generally lower in nutrients compared to biochars made from nutrient-rich biomass; primarily contributes carbon.
Hemp Biochar
Feedstock:
Hemp-Based: Sustainable Source
Production Process:
Pyrolysis: Produced through the pyrolysis of hemp biomass typically at temperatures similar to those used for wood biochar.
Modern Methods: Often produced using more controlled and efficient modern pyrolysis techniques.
Properties:
High Carbon Content
High Porosity: Generally has a very high surface area and porosity, which enhances its ability to retain water and nutrients.
Nutrient Content: Can contain higher levels of certain nutrients compared to wood biochar, depending on the hemp biomass used.
pH Level: Typically neutral to slightly alkaline, beneficial for balancing soil pH.
Food Composite
Hemp food composites are innovative materials created by combining hemp with other food ingredients or materials to enhance nutritional value, improve texture, and add functional properties. These composites utilise various parts of the hemp plant, and can be eaten raw or used to make milk, oil, cheese substitutes, or protein powder.
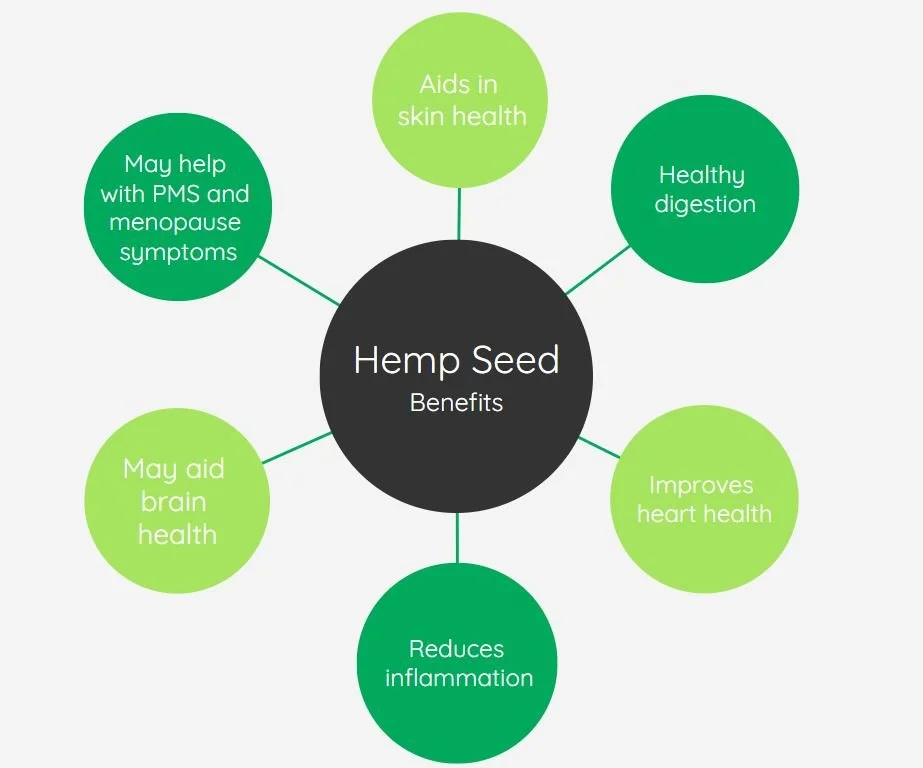
Hemp seeds are a highly nutritious food. They’re high in fat and rich in two essential fatty acids associated with reducing the risk of heart disease. Additionally, hemp seeds are a great source of plant-based protein, which makes up approximately 25% of their calories.
Animal Feed and Bedding
Hemp in Animal Feed
-
Hemp Seeds: Can be fed whole, shelled, or as a meal.
Hempseed Oil: Used as a supplement for its high fatty acid content.
Hemp Protein Powder: Added to feed for its high protein content.
-
Rich in Nutrients: Hemp seeds and hempseed oil are high in protein, essential fatty acids , and fiber. They also contain vitamins (like E and B vitamins) and minerals (such as magnesium, potassium, and iron).
Balanced Amino Acid Profile: Hemp provides a complete protein source with all essential amino acids, making it highly nutritious for livestock.
Improved Health: The fatty acids in hemp can enhance skin and coat health, improve immune function, and reduce inflammation in animals.
-
Livestock (Cattle, Pigs, Sheep): Hemp can be incorporated into their diets to improve overall health and growth rates.
Poultry: Hemp seeds and oil can enhance egg quality and poultry health.
Companion Animals (Dogs, Cats): Often included in pet foods and treats for its health benefits.
Hemp in Animal Bedding
-
Highly Absorbent: Hemp bedding can absorb more moisture than traditional bedding materials like straw or wood shavings, keeping the living environment dry.
Dust-Free: Reduces respiratory issues in animals, making it suitable for those sensitive to dust.
Biodegradable and Sustainable: Hemp bedding is environmentally friendly and can be composted after use.
Odor Control: Hemp has natural odor-controlling properties, making it ideal for animal enclosures.
-
Equine Bedding: Popular for horses due to its absorbency and low dust content.
Small Animals (Rabbits, Guinea Pigs, Chickens): Provides a clean, comfortable, and odor-free living environment.
Livestock: Used in barns and pens for cattle, sheep, and pigs.
Cannabinoids
Both hemp and cannabis contain cannabinoids such as cannabidiol (CBD), cannabidivarin (CBDV), cannabigerol (CBG), and others and therefore these cannabinoids can be extracted for either as their source. The most common cannabinoid is CBD.
CBD
CBD is an cannabinoid often consumed as an oil. Its benefits generally include pain relief and relaxation howevermore research is required into this.
The benefits of CBD do not change whether it is cannabis-derived CBD or hemp-derived CBD.
However, Hemp plants contain more CBD, than the cannabis plant which generally contains higher contents of THC making hemp a more appealing option for manufacturers.
Farming Hemp
The BHA has responded to the Defra Consultation: Health and Harmony: the future for food, farming and the environment in a Green Brexit which closed on 8 May 2018. Our contribution to this consultation is the first step towards creating a Hemp Farm Bill.
The BHA supports farmers and the hemp industry by educating and lobbying to remove current barriers, which dates back to legislation created in the 1960s and bring hemp into the 21st century. Our aim is to enable utilisation of the whole plant.
If you are interested in growing industrial hemp, you will need to apply to the Home Office for a cultivation licence. Please read this important Hemp Growers Information provided by the Home Office.
Follow the link below to learn more about Hemp Farming